LEOLAMP
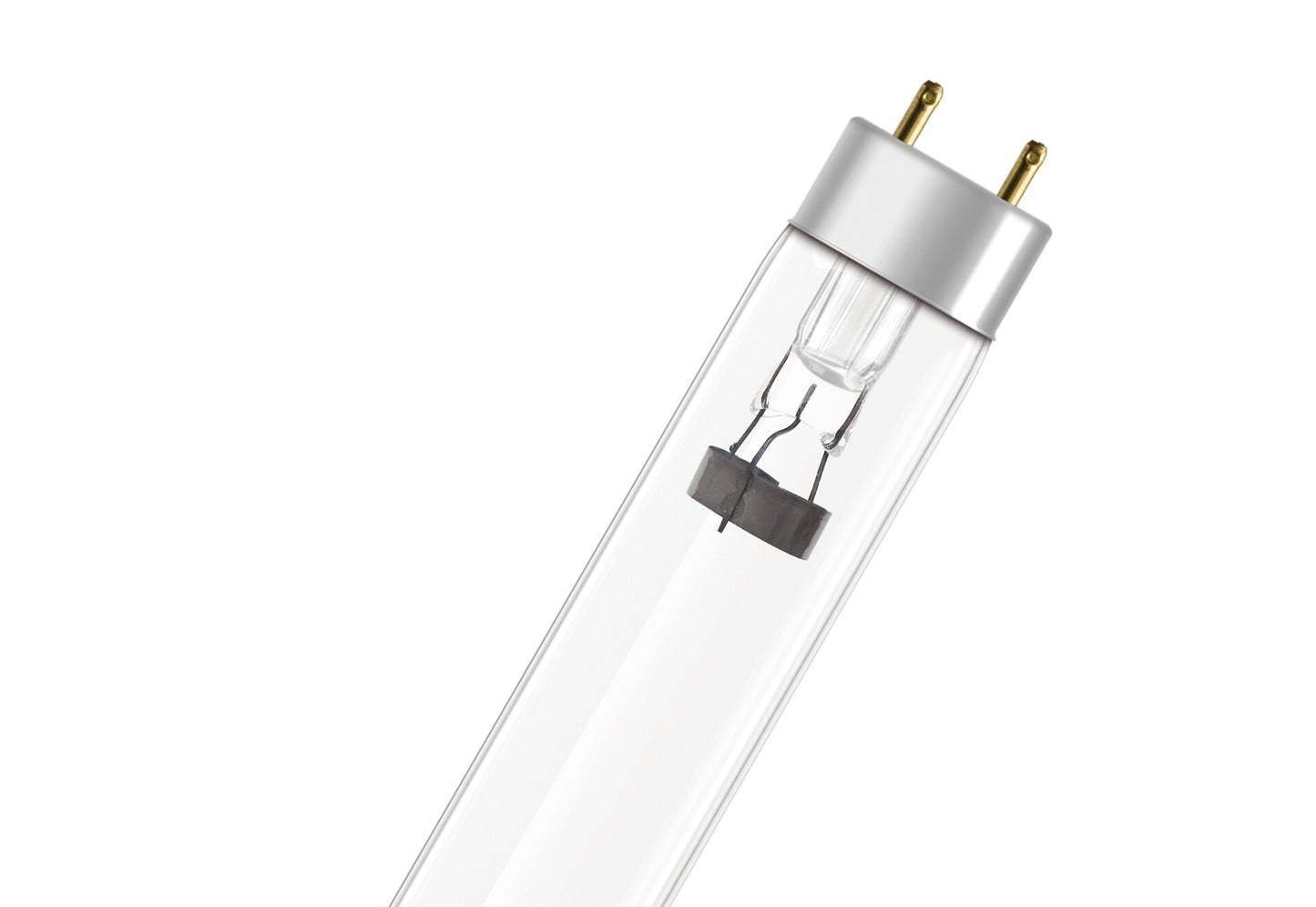
T8 LAMP For Ultraviolet Disinfection 18W / 36W
T8 LAMP For Ultraviolet Disinfection 18W / 36W
Couldn't load pickup availability
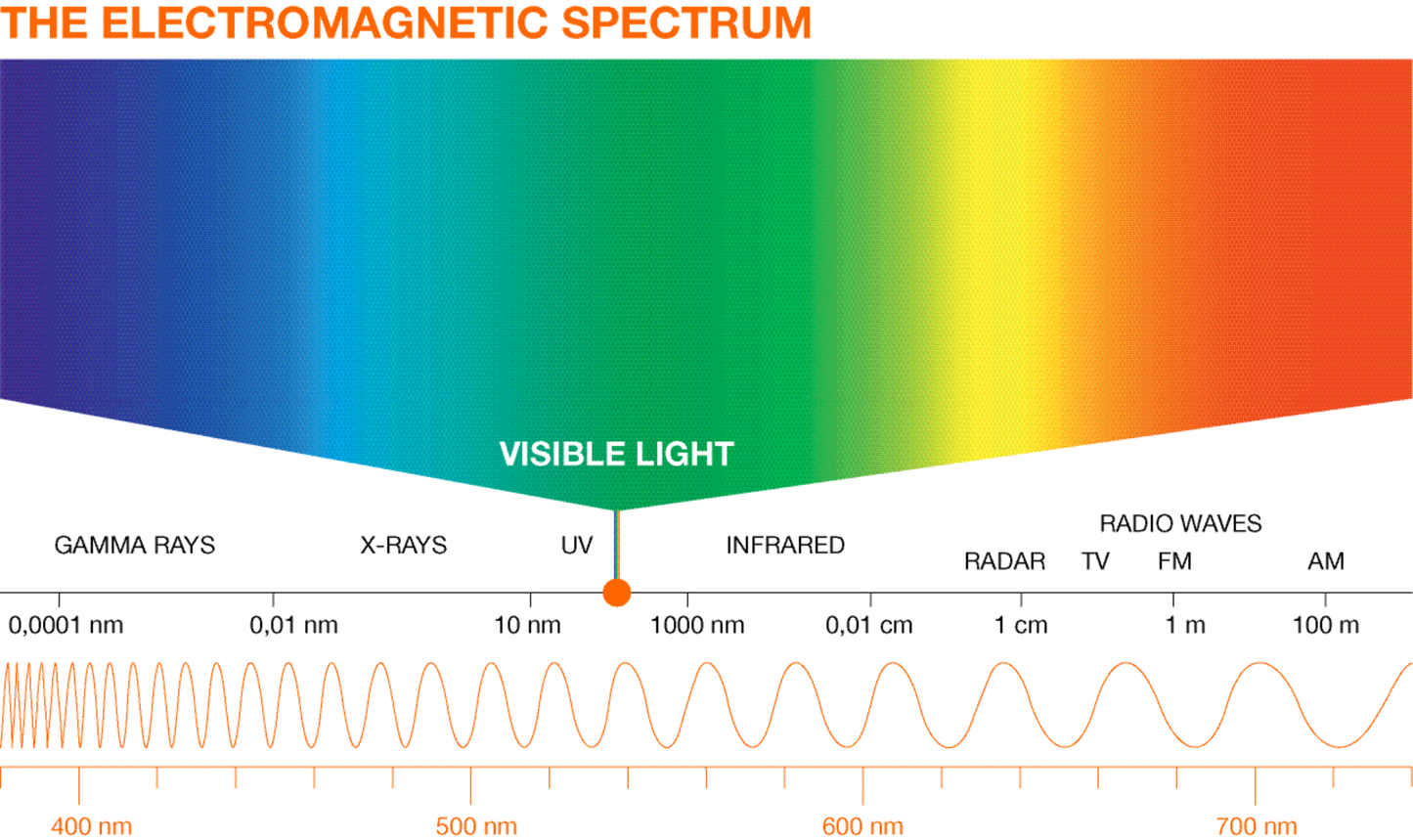
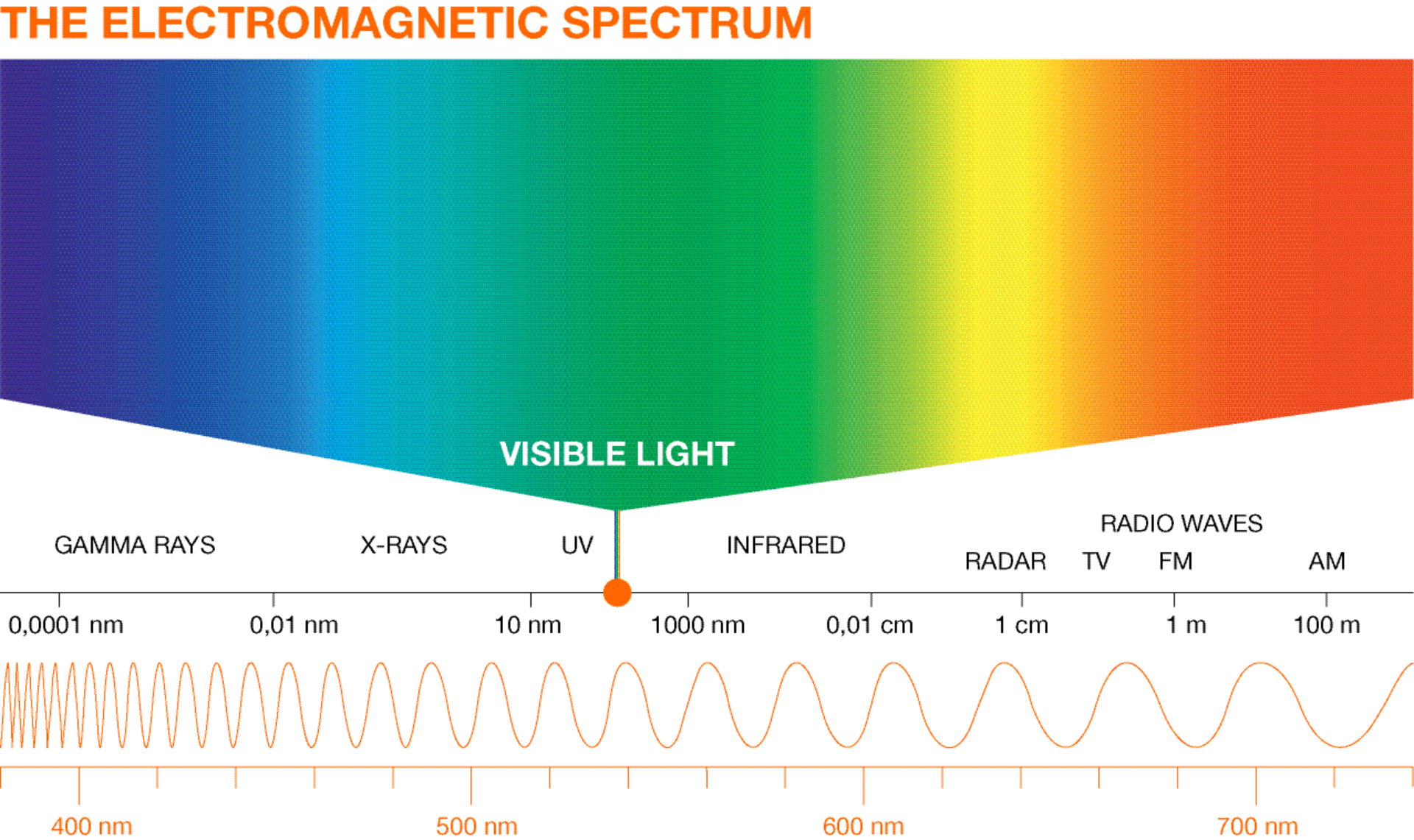
Electromagnetic radiation is characterized by a specific wavelength. When compared to visible light, ultraviolet radiation (UV radiation for short) has a significantly shorter wavelength. Depending on the type of UV radiation, it can be between 10 and 400 nanometers. UV radiation is divided into four ranges, depending on its wavelength:
- GRAPE: UV-A radiation has a wavelength between 315 and 400 nanometers. Light can cause some substances to fluoresce. Thanks to this capability, UV-A lamps have a long tradition of use in the entertainment sector, but are also used for forensic applications, for example to print banknotes with security marks. UV-A lamps can be produced simply and economically.
- UV-B: UV-B radiation has a wavelength between 280 and 315 nanometers. The light-emitting lamps in this range are highly appreciated by tanning enthusiasts in particular. UV-B lamps can tan human skin and are therefore widely used in tanning salons. Furthermore, they are used in medical applications, for example in the treatment of psoriasis.
- UV-C: UV-C radiation with a wavelength between 100 and 280 nanometers is classified as UV-C radiation. UV-C radiation has an exceptional property: UV-C radiation is very high in energy and is therefore capable of killing bacteria and viruses. The strongest effect against pathogens occurs at 265 nanometers. UV-C radiation causes considerable damage to the DNA of microorganisms, which ultimately leads to the decontamination of such pathogens. At this time, mercury vapor lamps are considered to be the most effective sources of UV-C radiation.
- I V: extreme UV with a wavelength between 10 and 100 nanometers is mainly used in manufacturing, for example in the production of chips.
UV-C radiation: environmentally friendly and efficient
Compared to other disinfection methods, UV-C radiation has numerous advantages:
- UV-C radiation does not require the use of toxic chemicals and compounds.
- Pathogens cannot create resistance to UV-C radiation.
- Radiation can render pathogens harmless in just seconds.
- The short duration of the treatment does not change the properties of a product.
- UV-C radiation does not leave residues or cause discoloration of surfaces.
- No ozone is produced in the corresponding range above 240 nanometers.
For these reasons, UV-C radiation has been used for decades in some sectors, such as medicine or the disinfection of food packaging (yogurt packaging, for example) as a clean disinfectant solution.
T8 UV-C lamps
- do not produce ozone during disinfection,
- are compatible with CCG and ECG,
- can be installed on a standard G13 support,
- last up to 20% longer than compatible competitive products (10,800 h/L70B50).
T8 UV-C lamps are available in three lengths: 440 millimeters (15 watts/25 watts), 900 millimeters (30 watts/55 watts) and 1200 millimeters (36 watts/75 watts).
Qty/Box 30
Materiais
Materiais
Dimenções
Dimenções
Como cuidar
Como cuidar